MicroRNA
MicroRNAs (miRNA) are highly conserved, short, single-stranded, non-coding RNA fragments that function in RNA silencing and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression.
They are typically 19-25 nucleotides in length and are derived from longer primary miRNA transcripts. MiRNAs regulate gene expression by binding to specific sequences, usually in the 3’-untranslated region (3’-UTR) of target mRNAs. MiRNAs can target multiple RNAs, allowing for fine-tuning of gene expression in response to various cellular signals.
miRNAs are involved in various biological processes, including cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. Dysregulation of miRNA expression has been linked to the development of various diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative disorders. An increasing number of studies have suggested that miRNAs could be potential biomarkers for cancer diagnosis and prognosis and potential therapeutic targets.
To study miRNA, we analyse your NGS data for differential miRNA expression, which can be visualised in different ways, such as volcano plots. We also check which pathways are most affected and which diseases the differentially expressed microRNAs play a role in. If total RNA-seq data is available, it can be analysed in combination with the microRNA data.
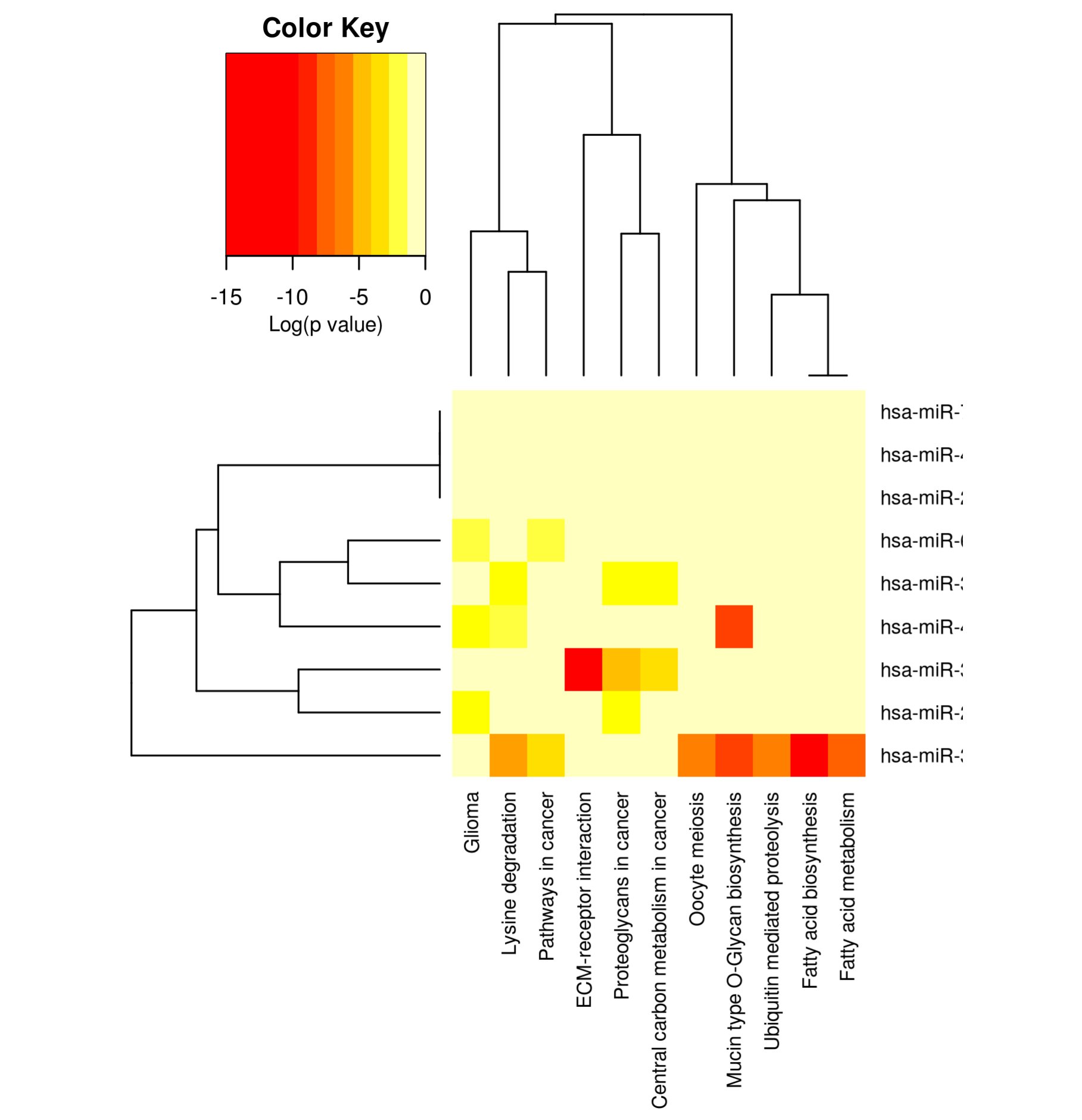
Heatmap to show the pathways affected by the most significantly miRNAs
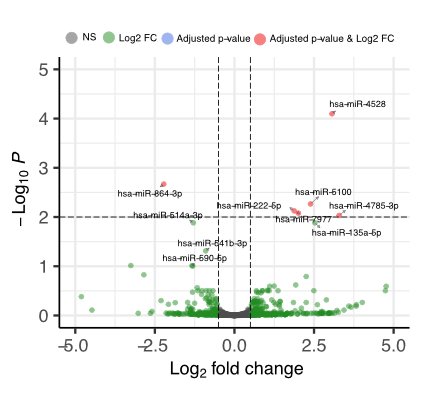
Volcano plot showing the most significantly different miRNAs

